REVA Medical is committed to advancing the field of bioresorbable scaffolds. Our goal is to provide information and techniques for success with BRS technology.
Implant Technique
Implant technique is the procedural steps taken to ensure proper placement, sizing, and apposition of coronary stents and scaffolds. Studies have shown that technique can impact outcomes for both drug eluting stents and bioresorbable scaffolds.
The REVA Technique
Right patient, right lesion
- Patients who are likely to benefit from BRS
- Patients who can comply to a full course of DAPT
- Lesions that can be adequately prepared
- Lesions without excessive tortuosity and calcification
Excellent preparation
- Pre-dilate the entire lesion with a non-compliant (NC) balloon using a 1:1 sizing ratio
- Prepare the lesion so that the balloon is uniform in appearance when fully inflated
- The goal is to achieve < 20% residual stenosis
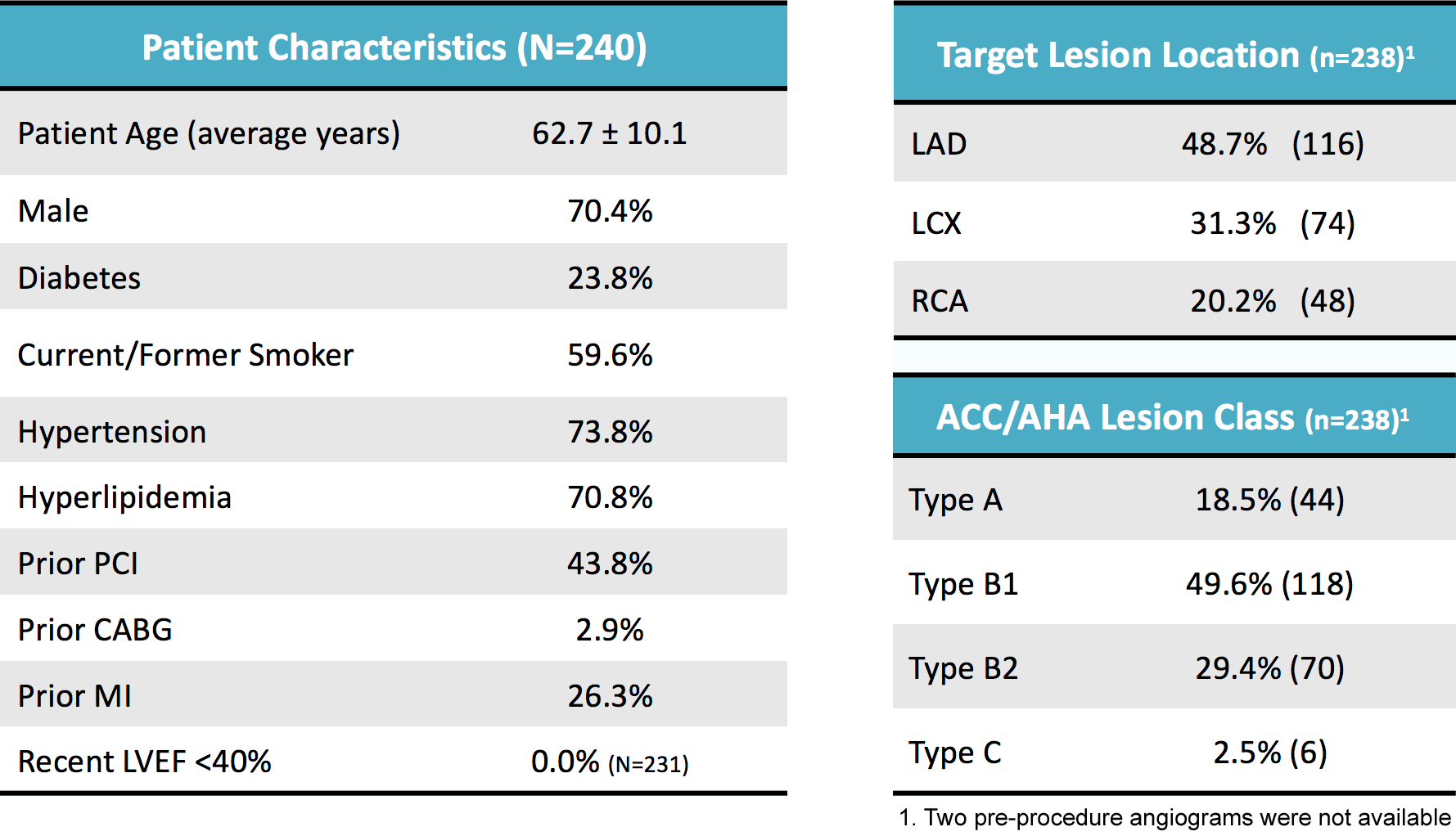
FANTOM II Patient & Lesion Characteristics1
Vessel to scaffold sizing
- Assess the average vessel diameter as well as the diameters of the proximal and distal vessel segments
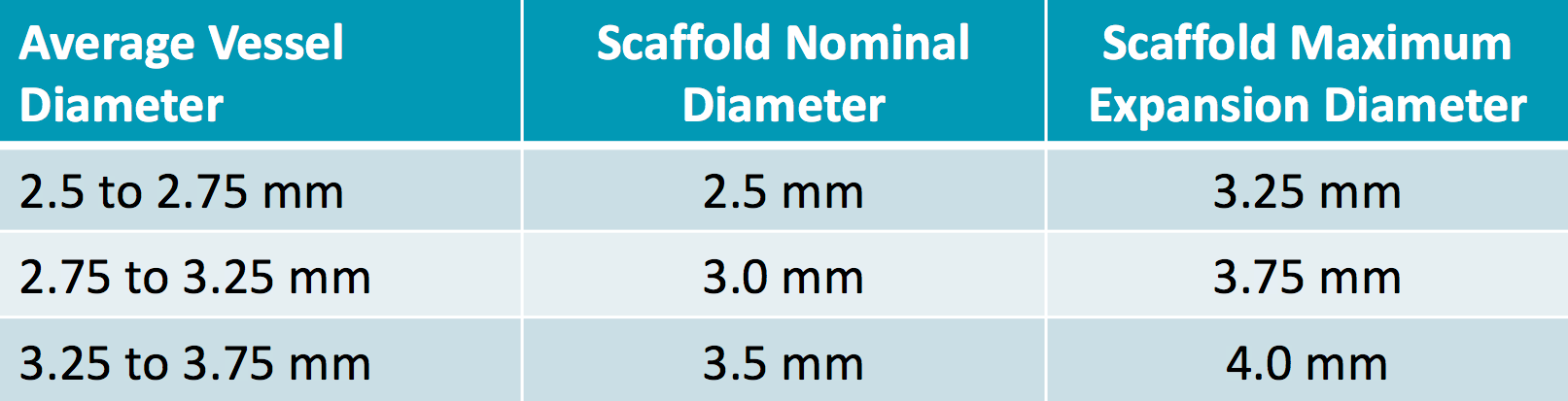
- Select a scaffold size based on the Fantom Sizing Chart
- No portion of the vessel segment should be less than 2.4 mm or greater than 3.75 mm
Apposition and expansion
- Post dilate the entire scaffold with a non-compliant (NC) balloon
- Use an NC balloon with a minimum 1:1 sizing ratio to the reference vessel diameter
- Inflate the non-compliant balloon to high pressure (≥ 16 atm)
- Do not exceed the labeled maximum expansion diameter of the scaffold
- Verify apposition to the vessel wall
Fantom Sizing Chart and Max Expansion Diameter
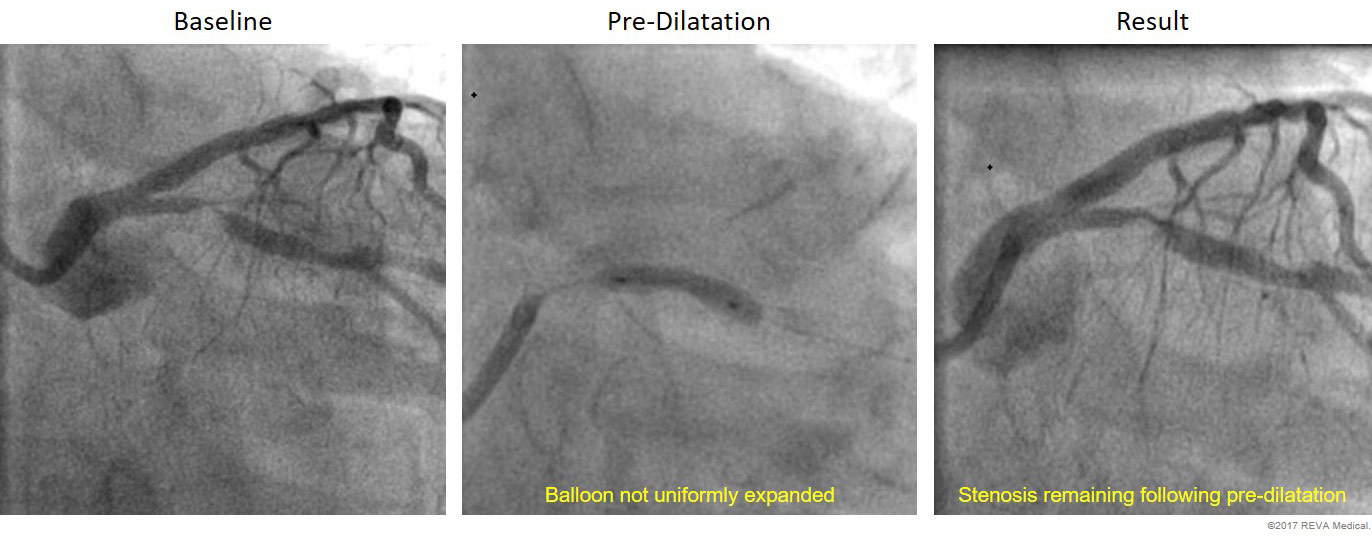
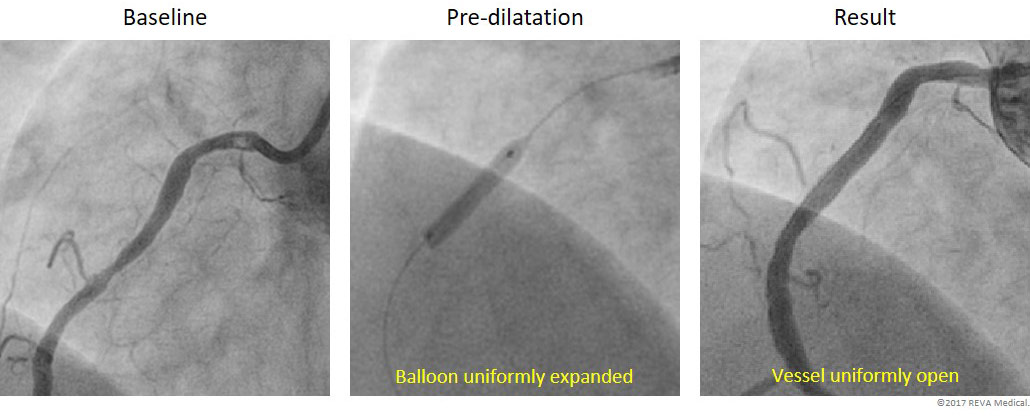
Lesion Preparation & Pre-dilatation
Lesion preparation is a critical part of BRS implant technique. It requires pre-dilatation with a non-compliant balloon in a 1:1 balloon-to-vessel size ratio. Look for even balloon expansion with less than 20% stenosis remaining after pre-dilatation.
Post-dilatation
Post-dilatation helps ensure that the BRS is completely expanded and apposed to the vessel wall. It requires a non-compliant balloon in a 1:1 balloon-to-vessel size ratio. The non-compliant balloon should be inflated to high pressure (> 16 atm) taking care not to exceed the expansion limits of the scaffold.
Examples of Malapposed & Apposed Struts
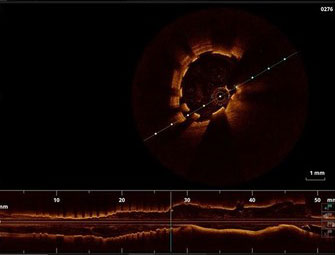
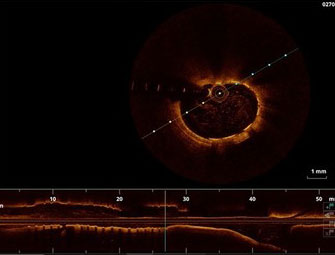
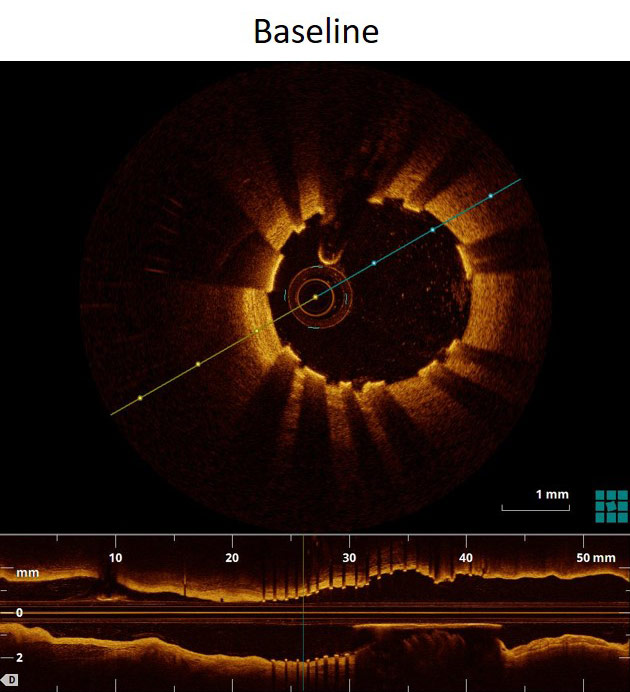
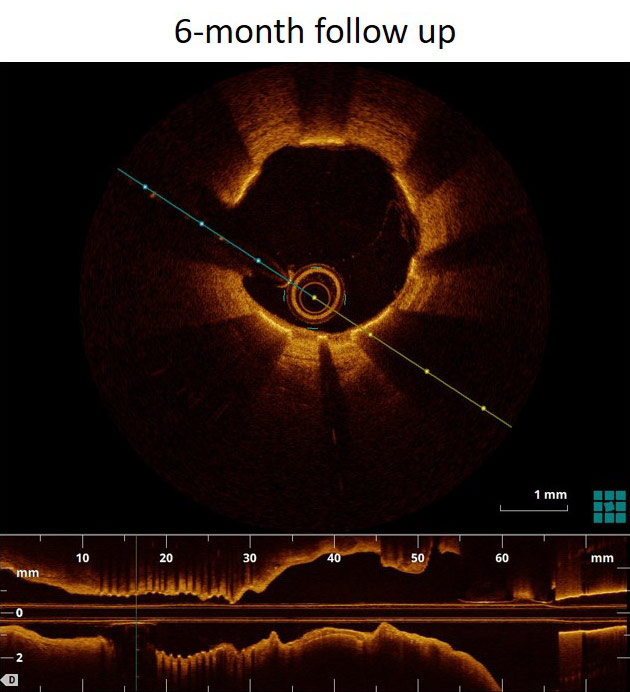
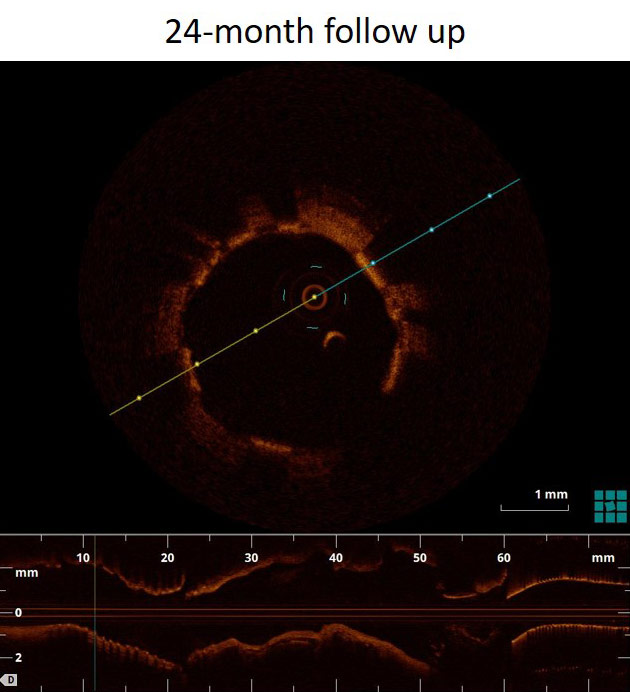
Angiography & OCT
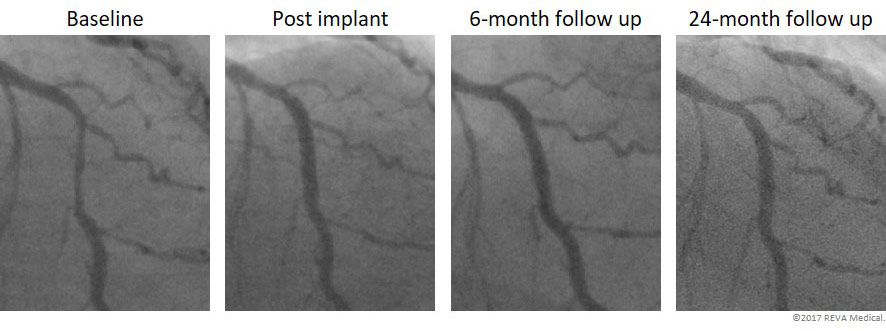
FANTOM II has one of the largest imaging and OCT data sets of any bioresorbable scaffold trial to date. These images provide a first-hand look at vessel healing and scaffold degradation at key time points.
Fantom Case: Angiographic follow up from FANTOM II
Fantom Case: OCT follow up from FANTOM II
References:
- Abizaid, A. The FANTOM II Study: First Report for the 12-month Clinical Outcomes of the Fantom Sirolimus-Eluting Bioresorbable Scaffold. EuroPCR 2017.